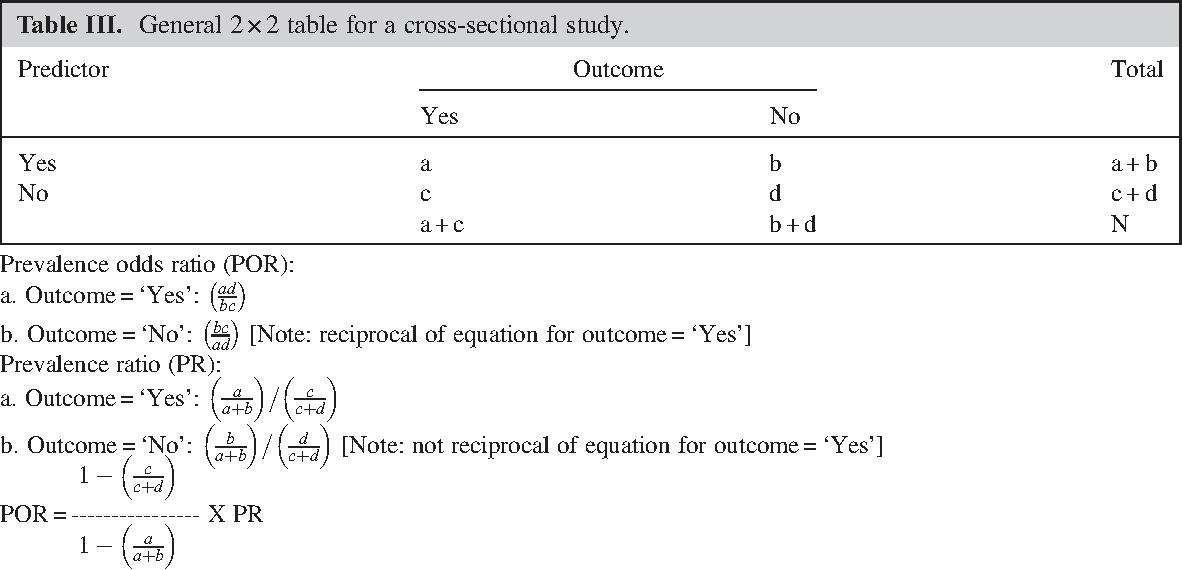
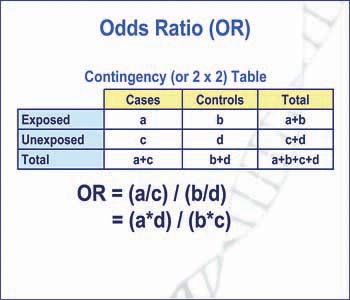
OR (a/c)/ (b/d) = ad∗cb The risk, or probability, and the odds are related with the following formula risk = Odds 1 odds from which we can infer that if the risk or the probability of failure is low ( P <01), then the OR is a good approximation of the RR, and they can be used interchangeably If the risk of the events is high, then theOdds Ratio (OR) The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with oddsThe observed odds ratio, 4, is not in the centre of the confidence interval because of the asymmetrical nature of the odds ratio scale For this reason, in graphs odds ratios are often plotted using a logarithmic scale The odds ratio is 1 when there is no relationship

Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Adjusted odds ratio vs odds ratio
Adjusted odds ratio vs odds ratio-Decimal odds represent the amount one wins for every $1 wageredValue As a verb rate is to assign or be assigned a particular rank or level or rate can be to berate, scold



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream
Odds (Safety) = 12/72 = 1787 Now get out your calculator, because you'll see how these relate to each other Odds (Accident) = Pr (Accident)/Pr (Safety) = 053/947 Understanding Probability, Odds, and Odds Ratios in Logistic Regression Despite the way the terms are used in common English, odds and probability are not interchangeableOdds Ratio Definition odds ratio – a measure of effect size, describing the strength of association or nonindependence between two binary data values In a case control study, this is the ratio between the fraction with the risk variant versus nonriskAn odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratio suggests a strong association
Odds ratio vs Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) Odds ratios are not very intuitive to understand, but are sometimes used due to convenience in plugging them in other statistics Where possible relative risk (risk ratio) should be reported due to it being much more a intuitive measure of effectiveness Still, odds ratios are widely used in fields likeThat can be expressed as a ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the number no of unfavorable outcomes, ie odds = number of favorable outcomes number of unfavorable outcomes Since there are 6 chances of you picking a green, and 4 chances of picking a red, the odds is 6 4 in favor of picking a greenThe odds ratio is reported as 1 with a confidence interval of (144, 234) Like we did with relative risk, we could look at the lower boundary and make a statement such as "the odds of MI are at least 44% higher for subjects taking placebo than for subjects taking aspirin" Or we might say "the estimated odds of MI were % higher for
Odds ratios work the same An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of XHas been to change the Odds of the man having the disease by multiplying the Prior Odds by the Likelihood Ratio 765 Calculating Likelihood Ratios The Likelihood Ratio (LR) can be calculated directly by using a quantitative assessment of the evidence, ie calculating the alternative probabilities of a given outcome, PFor example, if odds are 3/1 for the Cowboys this Sunday, then it is three times more likely that they will lose than win Odds of 31 indicate that if you bet $100, you will win $400, the original amount of your bet plus the profit Odds




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
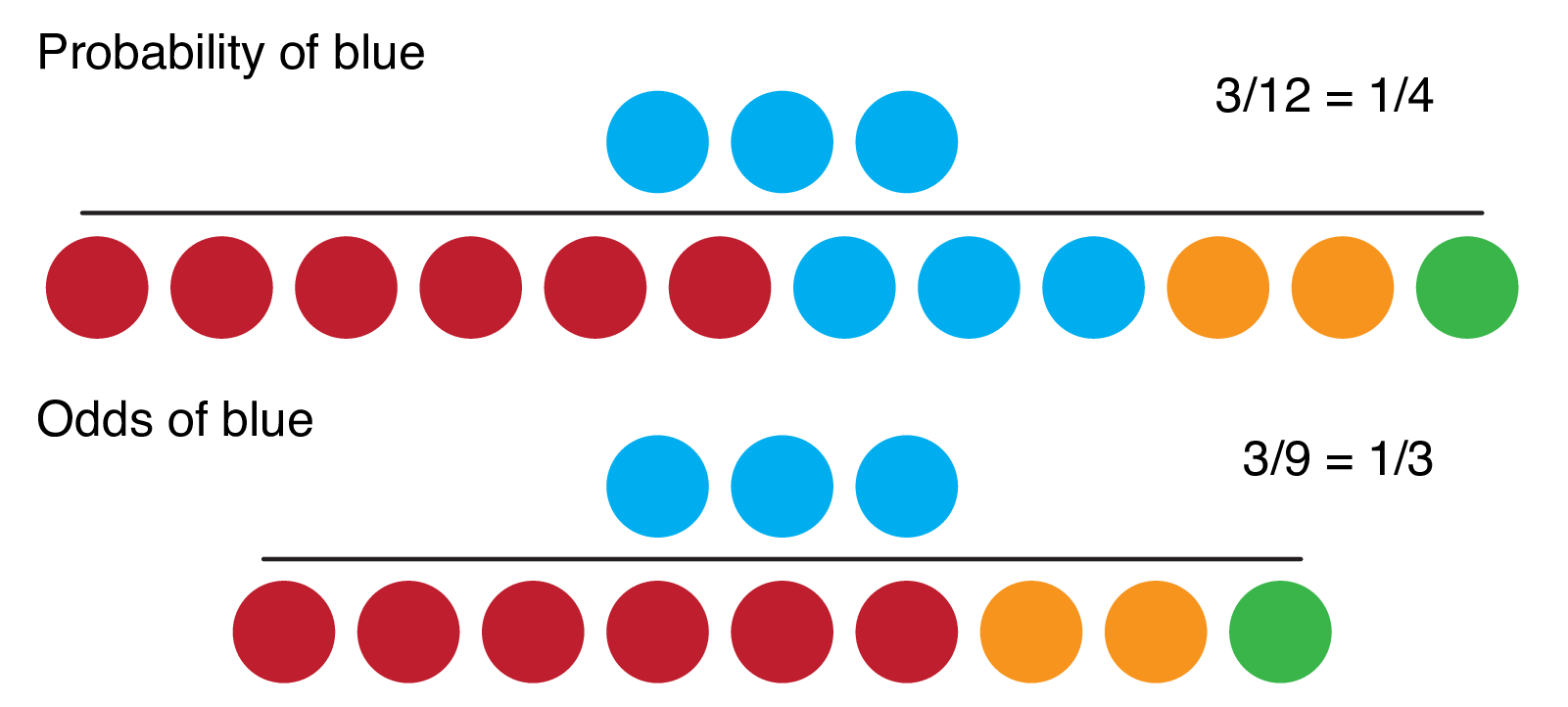
The difference between cats and dogs is 3 percentage points or 3 49 ≈ 612 % increase in probability for dogs over cats Meanwhile the odds ratio is 052 1 − 052 049 1 − 049 ≈ 1128 However I am finding a lot of social science literature intpreting O R − 1 as equivalent to increase in probability ExampleFigure2 Odds as a fraction Odds should NOT be confused with Probabilities Odds are the ratio of something happening to something not happeningIn our scenario above, the odds are 4 to 6 Whereas, Probability is the ratio of something happening to everything that could happenSo in the case of our chess example, probability is 4 to 10 (as there were 10 games3) The Odds Ratio 4) After calculating the odds ratio, we observe a 3fold difference in the prevalence rate (75% vs 25%) change to a 9fold difference in the odds ratio Clearly, the two methods produce opposing results Effect of Changing Incidence on OR Problem Let us consider the relationship between smoking and lung cancer




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow
The odds ratio is the ratio of two odds ODDS RATIO Odds Ratio = Odds of Event A / Odds of Event B For example, we could calculate the odds ratio between picking a red ball and a green ball The probability of picking a red ball is 4/5 = 08 The odds of picking a red ball are (08) / 1(08) = 08 / 02 = 4 The odds ratio for picking a redRisk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a 12 paperFractional odds are the ratio of the amount (profit) won to the stake;




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Pdf The Relative Merits Of Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Semantic Scholar
The odds ratio is the measure of choice in a casecontrol study (see Lesson 1) A casecontrol study is based on enrolling a group of persons with disease ("casepatients") and a comparable group without disease ("controls") The number of persons in the control group is usually decided by the investigatorOdds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probabilityThe odds of winning are 1/9,999 () and the probability of winning is 1/10,000 () In this case, odds and probability are essentially identical Relative Risk (RR) &



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
This is called the odds ratio;Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notLikelihood ratio = Posttest odds To use this formulation, probabilities must be converted to odds, where the odds of having a disease are expressed as the chance of having the disease divided by the chance of not having the disease



File Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Svg Wikimedia Commons




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Odds ratio of having disease for sector 2 vs sector 1 ( 35/44)/(22/95) = 345 (The odds of having disease living in sector 2 is more than 3 times of the odds for living in sector 1) Estimate and compare proportions of persons who contracted the disease by sector, using first 50% of the dataOdds Ratios and Log(Odds Ratios) are like RSquared they describe a relationship between two things And just like RSquared, you need to determine if thisE) But what about the Odds ratio?




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research
This StatQuest covers those subjects so that you can understand the statiIt is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratiosA more formal way of calculating posttest probabilities uses the likelihood ratio as follows Pretest odds ×




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Probability Odds Odds Ratio Youtube
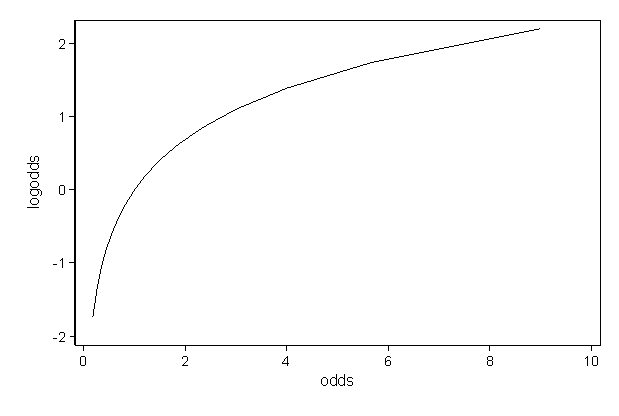
Odds ratio can be calculated either with odds of exposure or odds of outcome In casecontrol design, you would only know odds of exposure like you described In a different design, ratio of odds of outcome is the way to go These are the same mathematically which can be seen by playing with the 2 x 2 table Relative risk, risk ratio, orWhen the Odds ratio is above 1 and below 2, the likelihood of having the event is represented as XX % higher odds (where XX % is Odds ratio 1) That means that if odds ratio is 124, the likelihood of having the outcome is 24% higher (124 – 1 = 024 ie 24%) than the comparison groupThe odds aren't as odd as you might think, and the log of the odds is even simpler!




What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Odds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatmentThe odds ratio is extremely important, however, as it is the only measure of effect that can be computed in a casecontrol study design When the outcome of interest is relatively rare (<10%), then the odds ratio and relative risk will be very close in magnitude In such a case, investigators often interpret the odds ratio as if it were aThe Odds ratio is 14 x 9,999 Odds ratio = = 14 1 x 9,986 (this is a shortcut formula, only usable in 2x2 tables = n11×n22 n12×n21 where n11 is the upper left, n12 the upper right, etc) almost the same (it is the same if you round it like here) But now a little mathematical fact




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Odds Ratio Osmosis
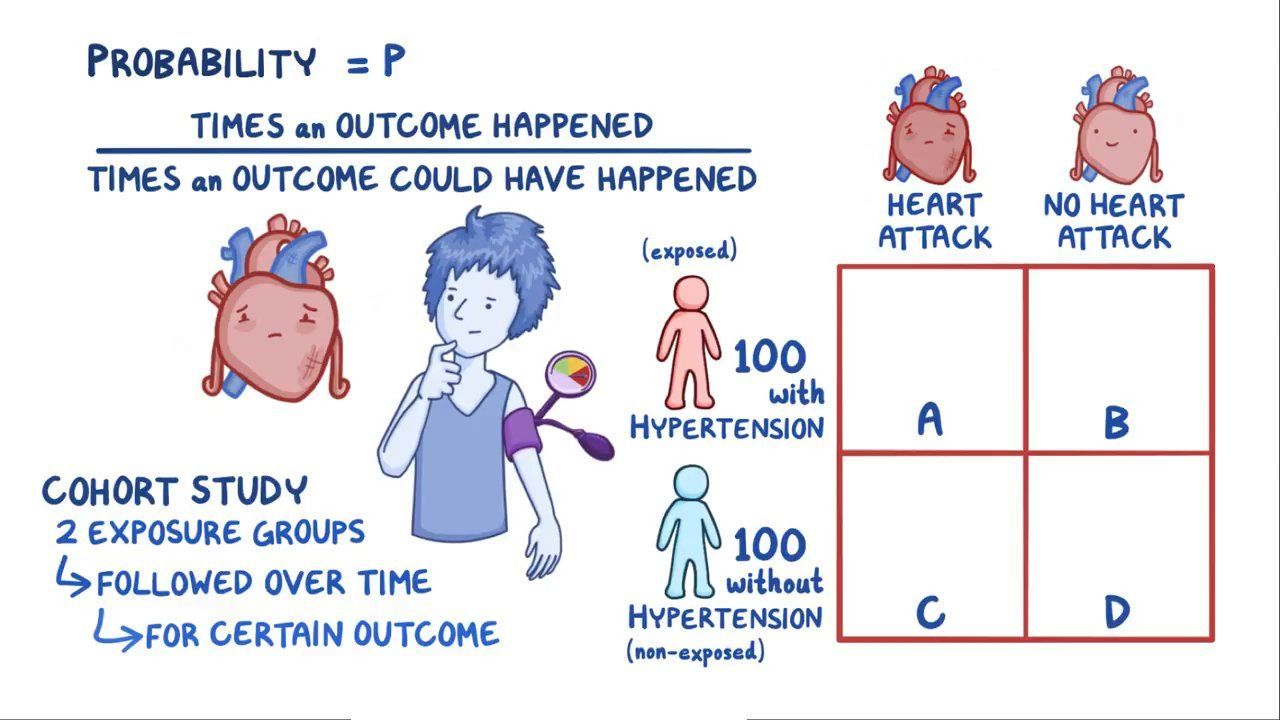
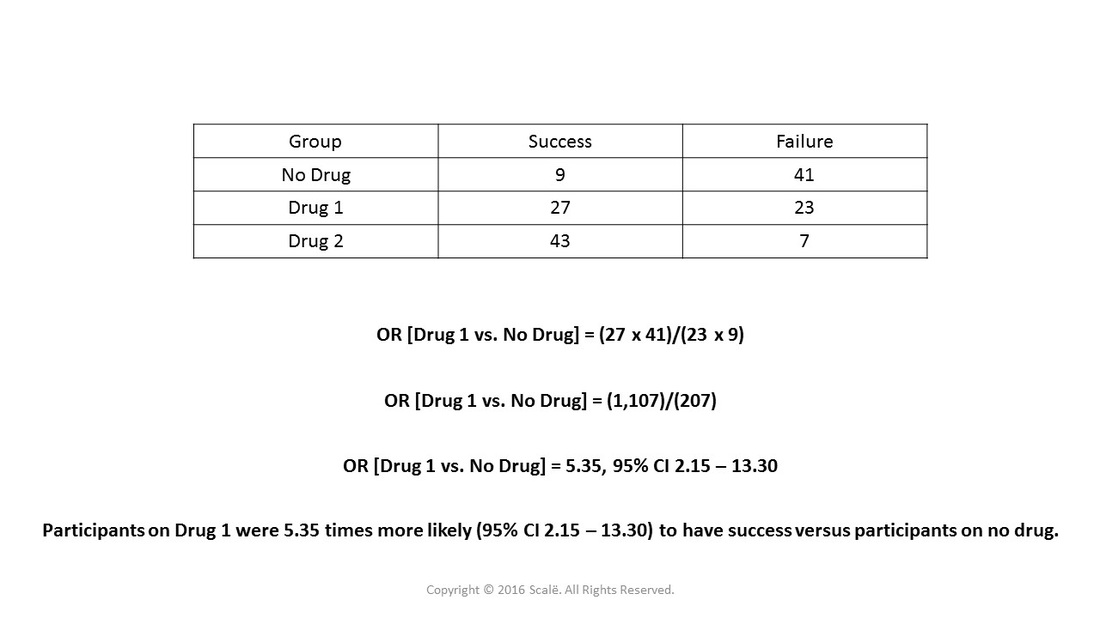
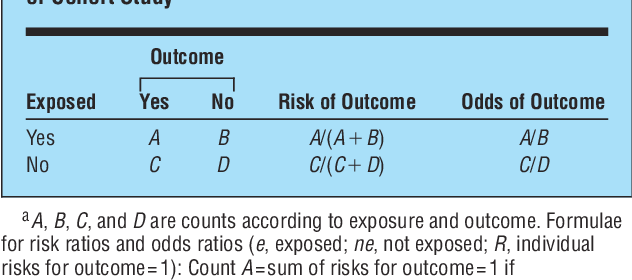
The term (Intercept) is an odds for the response Yi when Di=0 and Xi=0Depending the encoding, the other term(s) will represent odds ratios for the response for the specific (nonzero) levels of Di compared to 0 If Xi is continuous, the odds ratio is a ratio fo odds for groups differing by 1 unit in XiOn the other hand, a gambler backing Manchester United, who have odds of 1/5, will see a payout of just $1 for every $5 bet That means a total payout of $6 for someone betting $5 Bournemouth 5/1 Manchester United 1/5 You Bet $ on Bournemouth You Win $100 ( x 5=100) You also get your $ bet backThe odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



1
Log Odds Ratio Vs tfidf Vs Weighted Log Odds Recently, I was getting much excited about text analysis Few days ago Julia Silge introduced a new library called tidylo, which added more excitement to the task In this post, I'm going to show how we can isolate certain words from a set of documentsOdds ratios and logistic regression When a logistic regression is calculated, the regression coefficient (b1) is the estimated increase in the log odds of the outcome per unit increase in the value of the exposure In other words, the exponential function of the regression coefficient (e b1) is the odds ratio associated with a oneunit increase in the exposureWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR



Pdf Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar



Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World
The ratio of the odds for female to the odds for male is (32/77)/(17/74) = (32*74)/(77*17) = 1809 So the odds for males are 17 to 74, the odds for females are 32 to 77, and the odds for female are about 81% higher than the odds for males Now we can relate the odds for males and females and the output from the logistic regressionOdds ratio is the likelihood that an event will occur in relation to the likelihood that an event will not occur, 1 event for and 5 events against In Gambling, the odds are a ratio of the likelihood of a certain outcome, related to the other outcomes I had to look this up, because I forgot this part of finite math, from 25 years agoFractional odds are sometimes called British odds or traditional odds and are sometimes written as a fraction, such as 6/1, or expressed as a ratio, like sixtoone Decimal odds represents the




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf
Odds ratio in this example is found to be hight () (P<) (you can find an elaborate explanation on P value by clicking here) Having this high magnitude of odds ratio means that the association between these two variables is high ie texting while driving is highly associated with an increased occurrence of RTAAs nouns the difference between odds and rate is that odds is the ratio of the probabilities of an event happening to that of it not happening while rate is (obsolete) the estimated worth of something;Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out to




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download
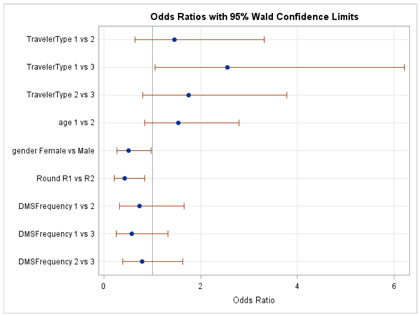



Public Perception Of Safety Messages And Public Service Announcements On Dynamic Message Signs In Rural Areas Appendix C Odds Ratio Graphs For Evaluation Of Hypotheses
Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Mixing Of Confounding And Non Collapsibility A Notable Deficiency Of The Odds Ratio American Journal Of Cardiology



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm




The Effect Of A Lack Of Dose Response Results On Odds Ratio Cross Validated



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression




Plotting Odds Ratio Vs Continuous Variable In Stata Stack Overflow




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
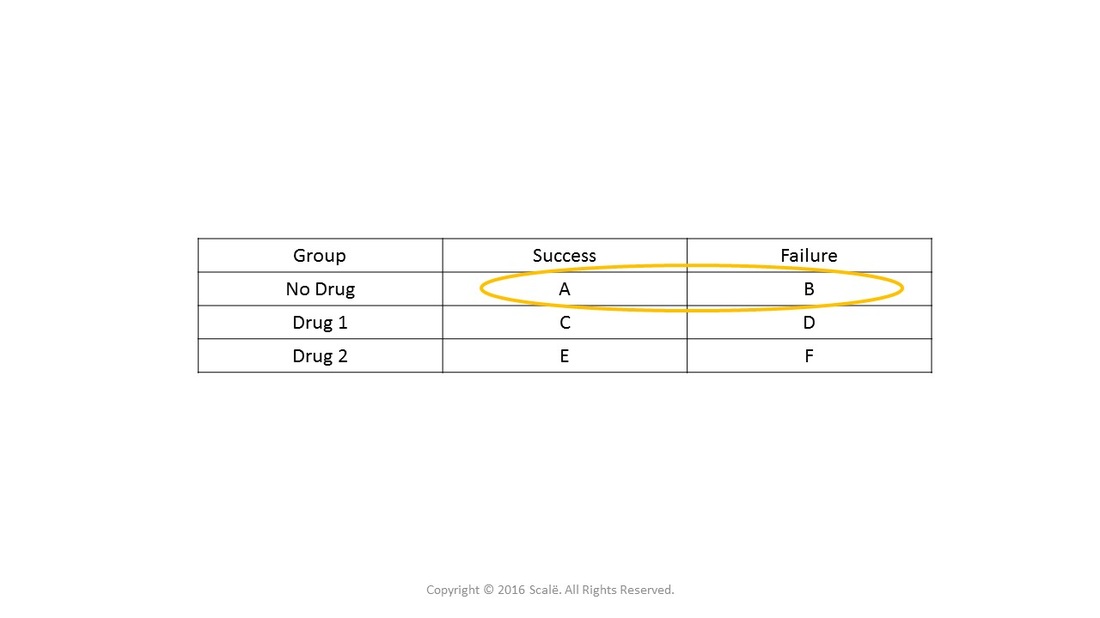



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss
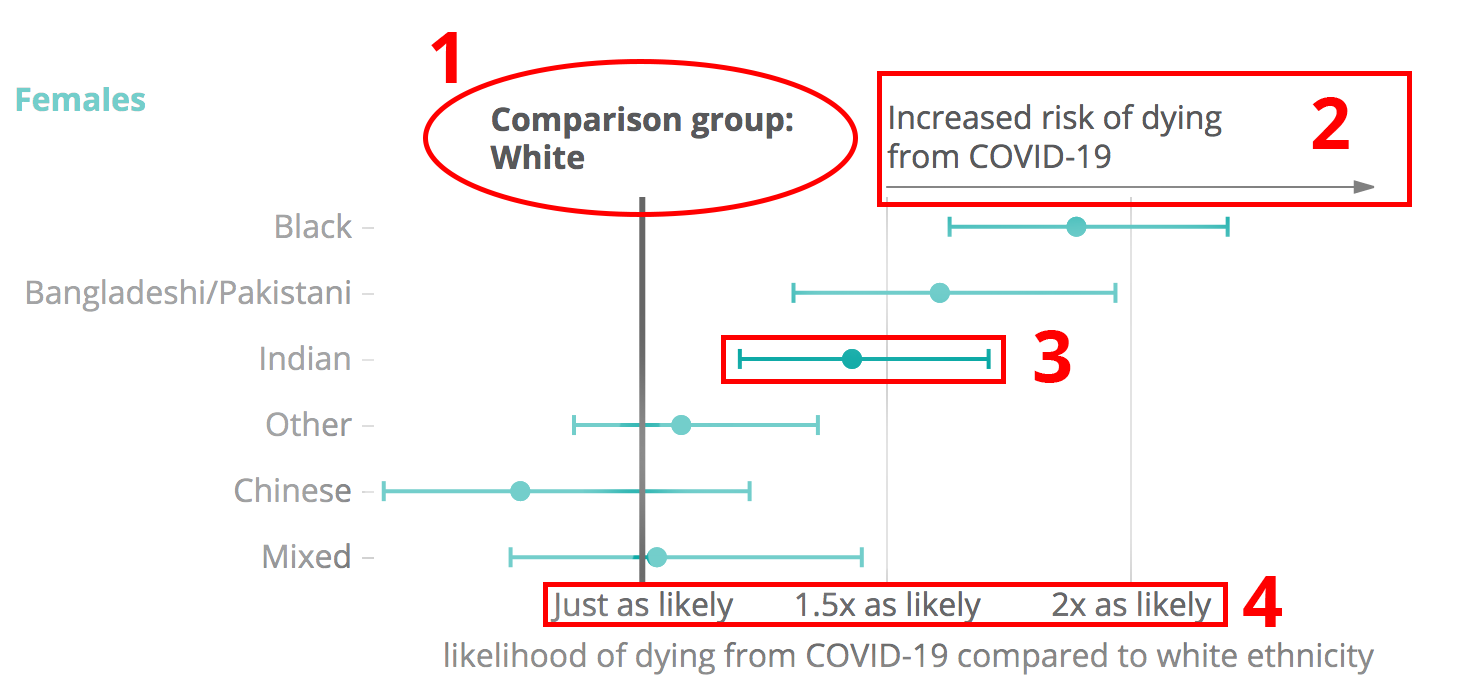



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February



1



Logistic Regression Odds Ratio




Cohort Specific And Meta Analysis Pooled Odds Ratios Ors Of Download Scientific Diagram




Diagnostic Odds Ratio Core Im Podcast
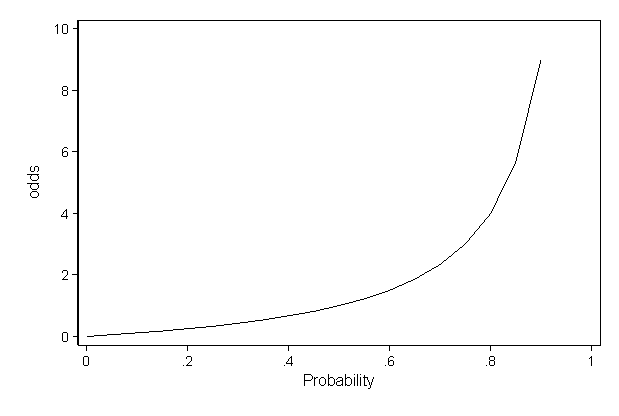



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression




Math3010 Week 6




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




What Is A Pooled Odds Ratio Quora




Crude Odds Ratios Cor And Adjusted Odds Ratio Aor And Their 95 Download Table




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
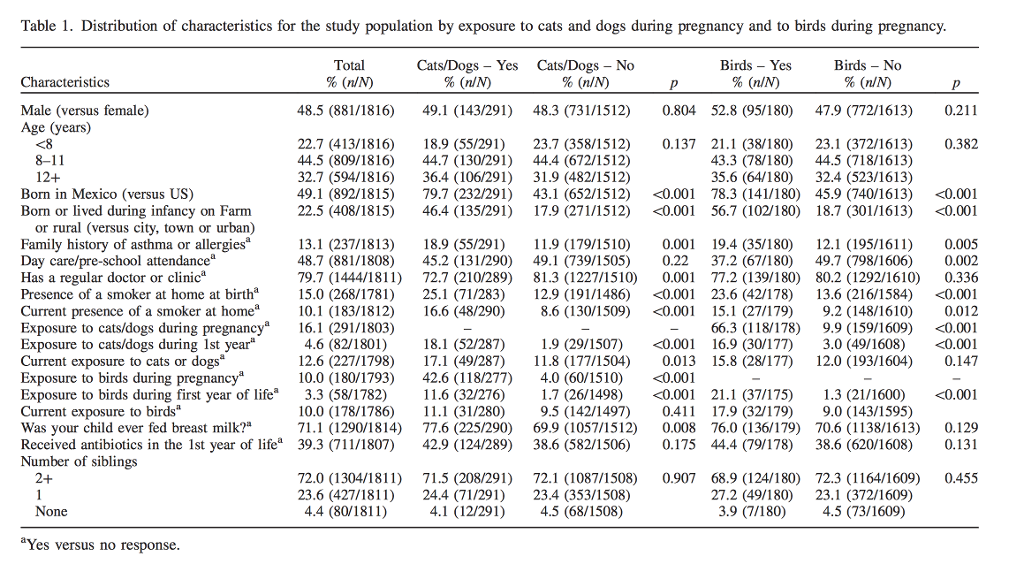



Calculating Odds Ratio Using Table 1 Calculate Chegg Com




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Graph Of Odds Ratio Versus Sleep Image Eurekalert Science News




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Adjusted Odds Ratio Definition Examples




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Wasp Write A Scientific Paper Using Excel 12 Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Sciencedirect



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Logistic Regression With Interaction Odds Ratio Interpretation Cross Validated
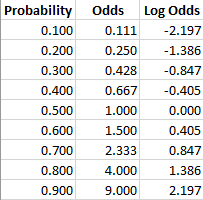



Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems
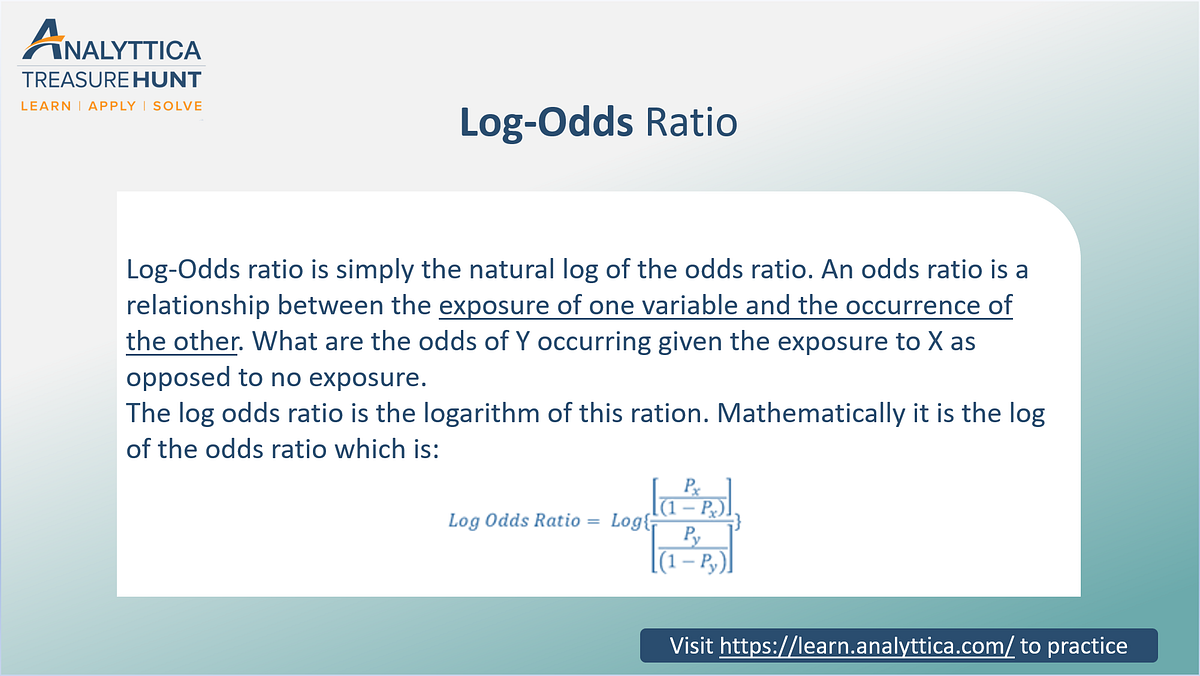



Log Odds Ratio Analytics Function Series By Analyttica Datalab Medium




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough
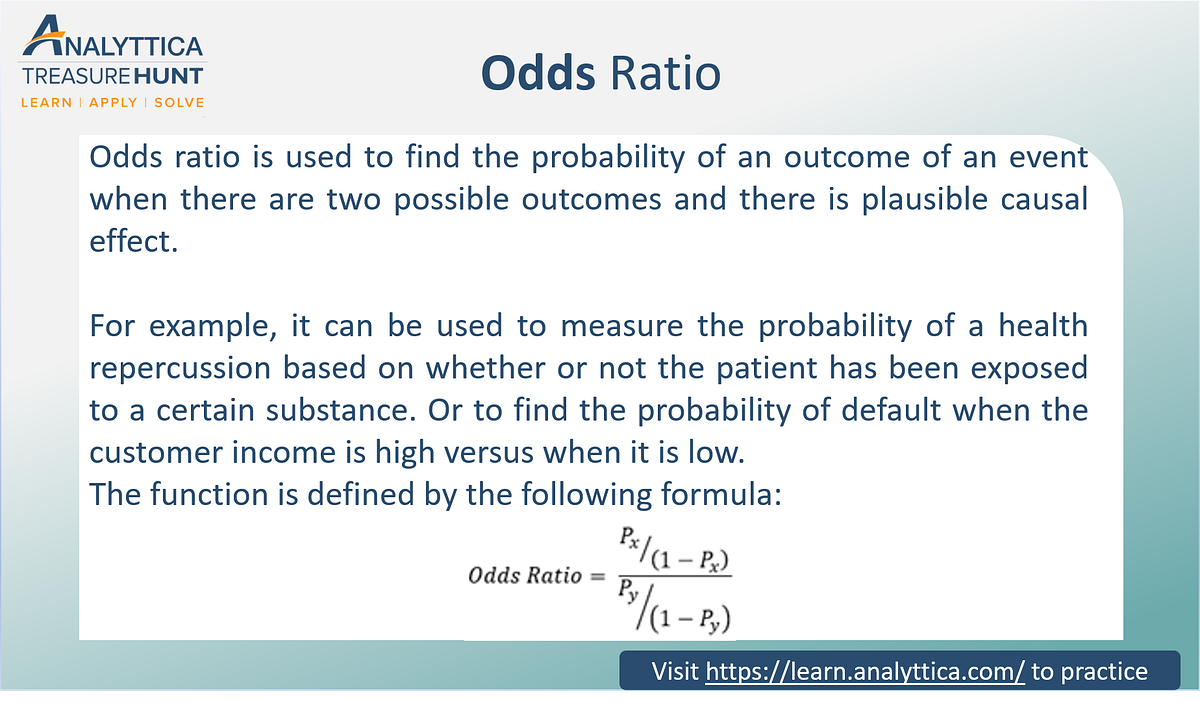



Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium




Joint Odds Ratios Ors And Interaction Odds Ratios Ior For G 9 E Download Table




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube



27 Sep 01 Draft




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Pdf The Relative Merits Of Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Semantic Scholar



Effect Modification Group C 1




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Diagnostic Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube Case Control Study Study Teaching




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



Odds Ratios Need To Be Graphed On Log Scales Andrew Wheeler




Strategies For Graphing Distributions Of Log Odds Estimates And The Corresponding Odds Ratios Cross Validated
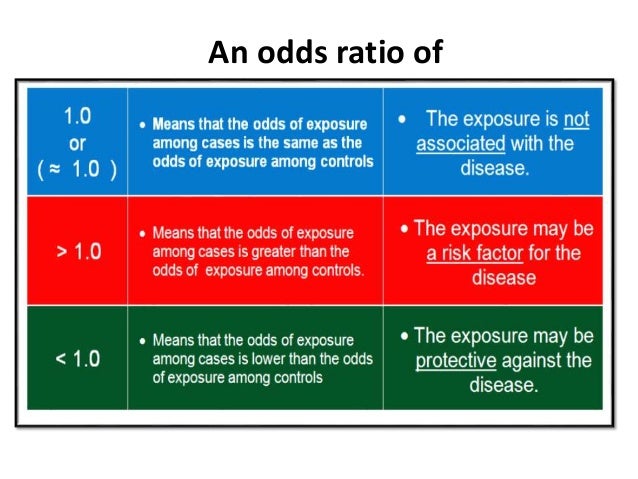



Odds Ratios Basic Concepts
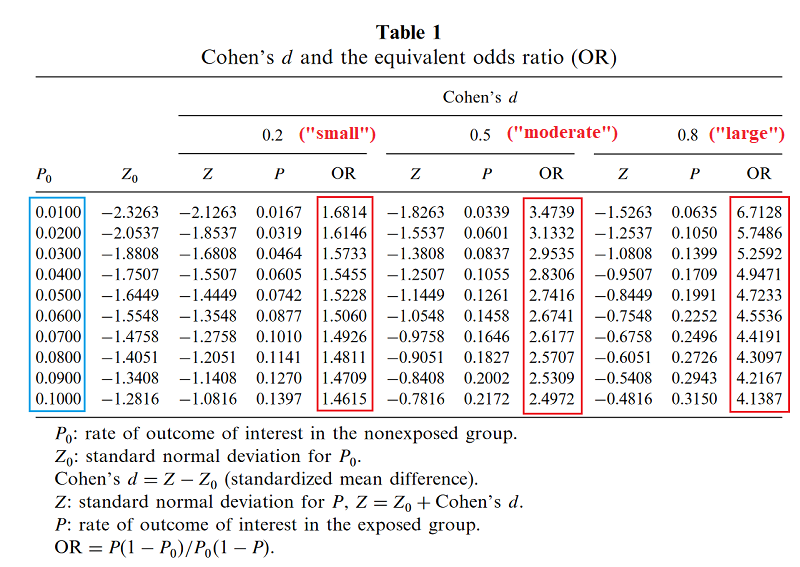



Never Tell Me The Odds Ratio Slate Star Codex




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
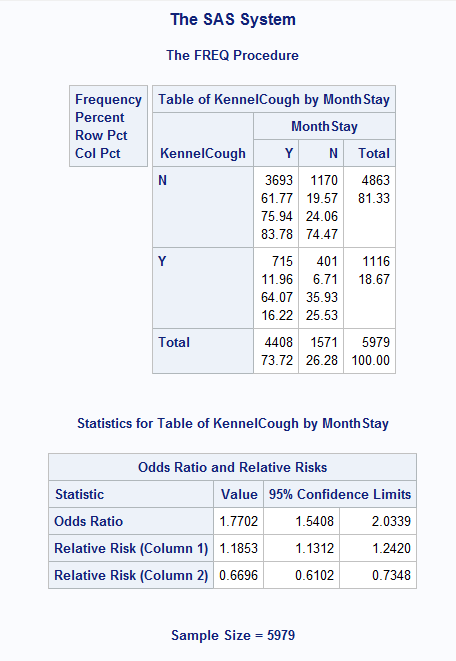



Different Odds Ratio From Proc Freq Proc Logisti Sas Support Communities




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases




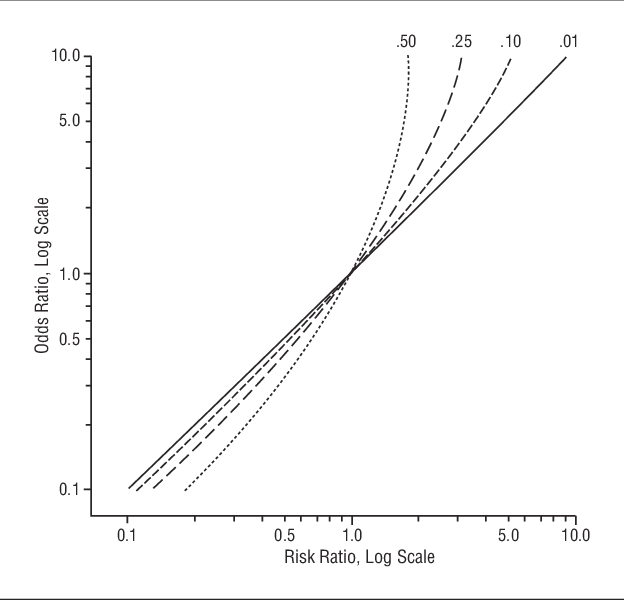
Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Odds Ratio Article
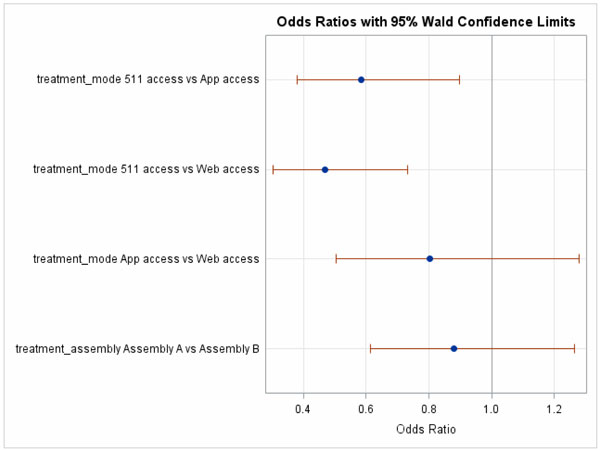



Effectiveness Of Disseminating Traveler Information On Travel Time Reliability Implement Plan And Survey Results Report Chapter 9 Data Analysis Fhwa Office Of Operations
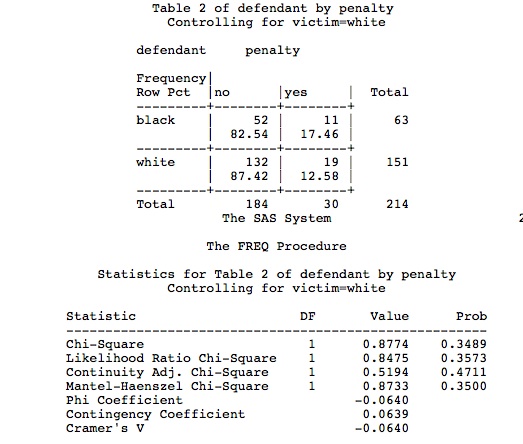



5 3 Marginal And Conditional Odds Ratios Stat 504




Figure 7 Random Effects Model Meta Analysis Of Relative Odds Ratio Of Icd Vs No Icd For Arrhythmic Death Between Younger And Older Subgroups Assessment On Implantable Defibrillators And The Evidence For




Figure 6 Random Effects Model Meta Analysis Of Relative Odds Ratio Of Icd Vs No Icd For Arrhythmic Death Between Women And Men Assessment On Implantable Defibrillators And The Evidence For Primary




How To Get Odds Ratio In Ordinal Logistic Regression Jmp User Community




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Q Tbn And9gcs7g3 Oy3gxo7fbk7uvklwexnnbqcmd7m5bqd Ghq64ww9hd4dh Usqp Cau
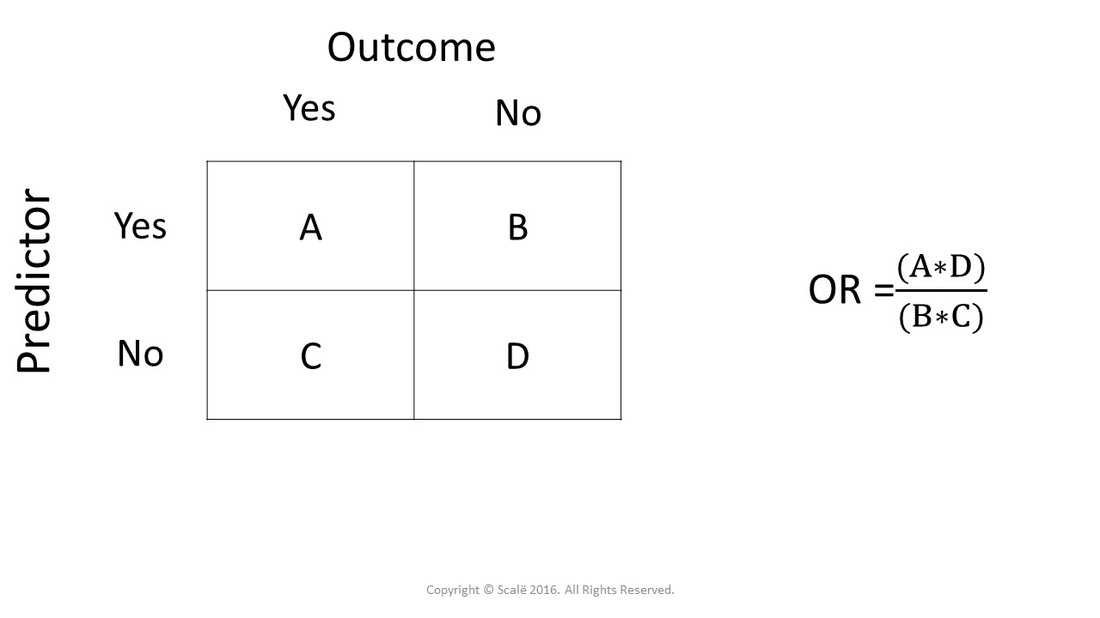



Calculate Odds Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿